How does whiplash occur? Symptoms. Dangers. What should you avoid? What can you do to recover as soon as possible? Read this post.
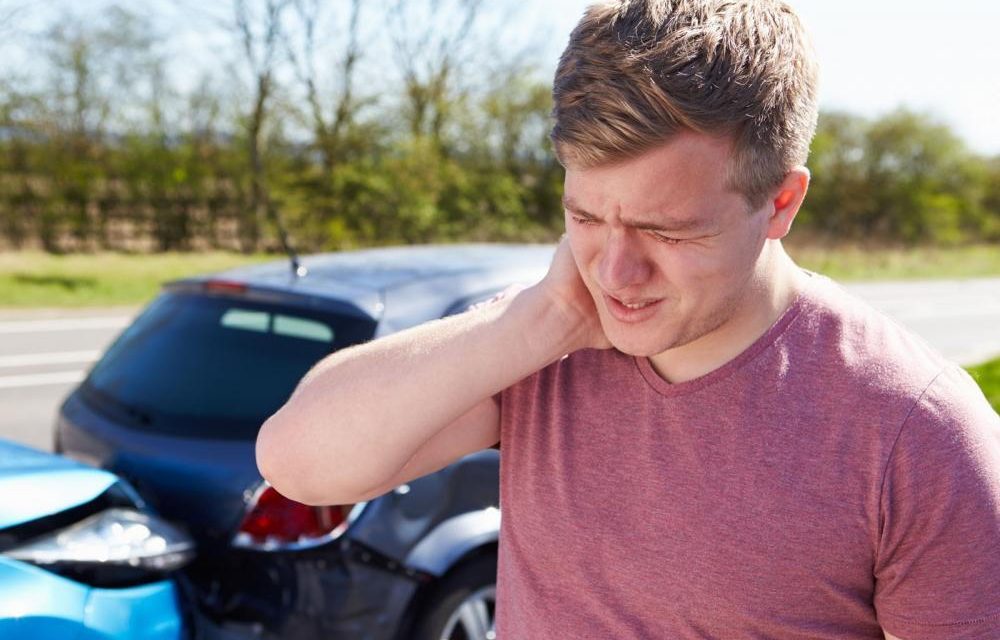
You were listening to music at a stopped traffic light, and suddenly it happened: a car almost entered through your trunk! It was very fast, like a movie. You came down saying you were okay. But while you were filling out the friendly report, your neck started to hurt. You have a whiplash.
Cervical whiplash is an injury caused by sudden neck flexion and extension.
The most common cause is a car accident. A typical accident is when the stopped car receives an unexpected impact from behind. As it is unexpected, the musculature is relaxed, and the play that the neck performs is greater. There is nothing that contains your head and neck.
The human head weighs about 8 kilos. At the moment of impact, the accumulated acceleration causes the weight to increase by more than 50 kilos.
It is not surprising that faced with such a magnitude of inertia, and our poor neck has a hard time.
Symptoms of a whiplash.
Whiplash. Pain and contracture.
Whiplash. Neck Pain. Pain and contracture.
They appear after a collision in the rear of the car:
- Neck pain that appears immediately or in the hours after the accident.
- Neck stiffness.
- Headache (headache). Usually in the back of the head.
- Muscle contractures in the neck and upper shoulders can accompany neck pain.
- Sometimes there may be pain that radiates to the arms. (Go down the arms.)
- Dizziness or instability, vertigo. As I call it: the “glass of cava” effect.
⇒All these would be the most common symptoms of whiplash or also called a cervical sprain.
But there may also be other lesser-known symptoms of whiplash:
- Low back pain.
- The appearance of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Post-traumatic stress syndrome.
- Emotional stress With anxiety and driving phobia.
- Auditory tinnitus. (Ringing in the ears).
Vertigo or instability. You can read more about the subject at this link: Vertigo and cervical wear. What is true?
Usually, in the face of minor whiplash, we will stop having symptoms in a few days. With rest, ice deflates structures or mild heat to relax. With painkillers and mild anti-inflammatories, we will get better soon. This would be the basis for a cervical sprain.
Low magnitude?
It is imperative to have common sense in this life. It will not be the same to attend to someone who goes to the emergency room on their own two days after having an accident as someone brought by ambulances, and the health technicians tell you that the patient was miraculously saved.
I always ask how the accident happened:
- How fast was the car going?
- If he was wearing a seatbelt.
- Did the airbags go off?
- Did you get out of the car on your own?
- If Were there serious injuries?
- Did someone die in the accident…?
You will give me why in a multi-car crash, the one that will receive the most significant impact will be the last in the row. Or that if the car were a total loss, the impact would have been of category.
Well, that’s common sense.
Neck pain: It hurts a lot, and I’m stiff. I go to the emergency room. What will they do to me?
The medical examination is the most important.
Cervical X-rays will also aid in diagnosis. But they will not be of vital importance. Sometimes only a cervical rectification or signs of wear or previous osteoarthritis existing before the whiplash is observed.
The myth of the cervical collar.
I have been caring for patients who have suffered from whiplash for twenty years. Only rarely do I prescribe a cervical collar. When I did it, I highlighted the need to remove that collar in a maximum of 72 hours.
The cervical collar is addictive and causes atrophy of the cervical musculature (weakness of the musculature), which will only worsen whiplash symptoms.
It can be looped. It hurts; I’m wearing the collar. I atrophy. I can’t hold my head. I put on the collar! It is the cause of a chronification of symptoms.
Cervical collar: less is more!
The patient will leave the emergency room with a whiplash diagnosis and a follow-up appointment with the traumatologist, rehabilitator or family doctor.
But you will have the uncertainty that you will not know how long it will take to recover…
Then a significant problem is added…
Whiplash is an entity where family doctors, rehabilitators, traumatologists, physiotherapists, osteopaths, masseurs, psychologists, experts, lawyers, coroners and insurers find it difficult to agree—the ghost of economic compensation clouds the atmosphere. Let’s put these peculiarities aside.
Whiplash warning signs. You should immediately consult the emergency service.
Cervical pain (neck pain) right away.
· sensation of instability of the head. They are patients who arrive at the emergency room holding their necks.
· Immediate appearance of “electric current” or loss of strength or loss of sensation in the arms or legs.
Head injury with loss of consciousness.
Once in the consultation, what?
Cervical pain or neck pain: weapons to overcome it
Whiplash. where can hurt
Other types of complementary tests may be necessary:
1. Functional radiographs. They should be performed with the neck in flexion and extension. They will give us information to determine if there is a cervical sprain and if there is a real possibility of vertebral dislocation.
2. NMR Cervical nuclear magnetic resonance. It will give us information on the state of the discs and ligaments.
3. Sometimes, it may be necessary to perform an EMG Electromyogram to check the condition of the nerves in the arms.
4. Going to the rehabilitation doctor will be vital in reducing the period of discomfort. Under medical or specialist supervision, begin to do gentle mobilizations and isometric exercises to strengthen the neck muscles.
Starting rehabilitation as soon as possible shortens the recovery time from your whiplash.
Whiplash, did you know that…
Why are there more shockers than shockers with whiplash? Because when someone is going to collide, they tense the cervical muscles, and there is less movement of the neck.
Below 14 km/hour (38.8 meters/second), there is no possibility of whiplash. There will be no neck pain.
There is more pain in extension than in flexion because the sternum acts as a stop in flexion.
It is imperative to keep the height of the head well graduated. Because in the case of whiplash, it will prevent the inertia of the neck from breaking our necks. (I attended a car accident where a high-end vehicle full of airbags could not do anything in the face of a poorly adjusted headrest. The deceased died of a high cervical injury, a cervical dislocation or fracture…)
The disc level that suffers the most in the face of whiplash is cervical C5 and C6.
It has been shown that attending the physical therapist early shortens the recovery time.
Being a woman over 60 years of age worsens the prognosis.
Suffering from previous cervical osteoarthritis, prior spinal surgery, and having the neck rotated at the time of impact worsens the healing prognosis.