Home canning is a great way to preserve food, but this can be dangerous if the canning process is not done safely, as it could cause botulism.
Botulism is a rare but severe illness caused by a toxin that attacks the nervous system. This toxin is produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. Improperly packaged, preserved, or home-fermented canned foods can create the ideal conditions for bacteria to produce toxins. When this situation occurs, the food does not change its smell, flavour or colour, so it cannot be detected when tasting it. A small amount of food with this toxin can be deadly. Botulism is a medical emergency; if it is suspected, you should go to a medical center immediately.
Causes
Clostridium botulinum lives in soil and non-potable water; it produces spores that survive in poorly preserved or canned foods, where they generate a toxin. The most frequently contaminated foods are home-preserved vegetables or fruits, cured pork and ham, raw or smoked fish, and honey.
Botulism can also develop if the bacteria enters through wounds and produces the toxin there, like tetanus.
Infant botulism occurs when live bacteria or spores are ingested and grow within the infant’s gastrointestinal tract. Its most common cause is the ingestion of honey.
Botulism, causes and treatment: laboratory analyzing canned food
Symptoms
Symptoms appear between 8 and 36 hours after contact with the toxin. All types of botulism can be fatal and are considered medical emergencies. It is a disease that is not accompanied by fever.
There are three forms of botulism:
food botulism
It is transmitted by food. Home canning, if not done correctly, offers the ideal conditions for Clostridium botulinum to reproduce and produce botulinum toxin. In general, the signs and symptoms of foodborne botulism begin between 12 and 36 hours after ingestion of the toxin. But, depending on the amount of toxin consumed, the onset of symptoms can range from a few hours to a few days. The signs and symptoms are:
They are drooping the eyelids.
Trouble breathing.
Nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramps.
Paralysis.wound botulism
If the bacteria enter through a break in the skin, they can cause a dangerous infection similar to tetanus. The wound may or may not appear red and inflamed. The signs and symptoms of wound botulism appear about ten days after the toxic substance has entered the body. The signs and symptoms of botulism are:
droopy eyelids
Difficulty breathing.
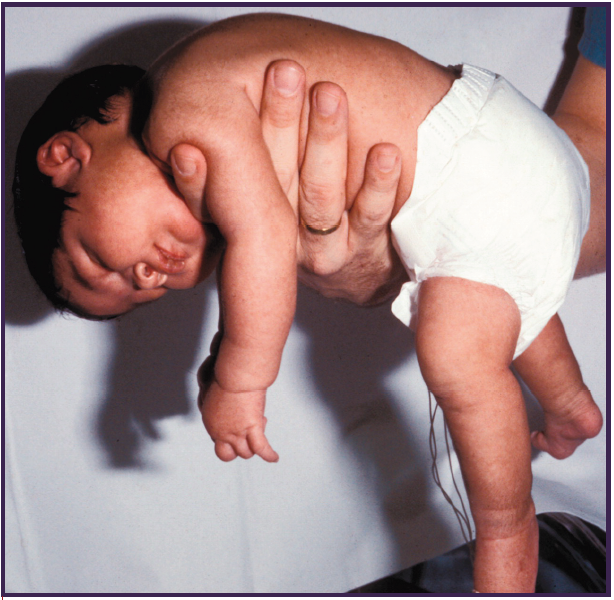
Paralysis.infant botulism
It is the most common form of botulism and begins when the bacteria Clostridium botulinum spores grow in the baby’s intestinal tract. It usually occurs in babies 2 to 8 months old. Infant botulism is linked to food, such as honey. Symptoms begin within 18 to 36 hours after ingestion of the toxin. The signs and symptoms are:
Constipation (it is the first thing that appears).
Muscle weakness and trouble holding your head.
Weak cry.
Irritability
drooling
droopy eyelids
Fatigue
Difficulty sucking or feeding.
Paralysis.Blood tests detect the toxin and stool cultures (stool culture).
Treatment
Treatment is based on the administration of botulinum antitoxin. If there is difficulty swallowing or respiratory distress, the child should be admitted and helped to breathe through mechanical ventilation and to eat through a tube. With proper treatment, the child can overcome the disease.
How to prevent botulism caused by home-canned canned food?
We can prevent botulism from home canning by following these tips:
Use proper techniques for canning preserves.
Have the right equipment for the type of food you are canning: Low-acid foods are one of the most common sources of home-canned food-related botulism. These foods have a pH greater than 4.6. Low-acid foods include most vegetables, some fruits (such as tomatoes or figs), milk, meats, fish, and shellfish. Pressure canning is the only recommended method for canning low-acid foods.
Do not use packaging of boiling water for low-acid foods.
Use approved pressure canners and follow the manufacturer's instructions.What you should know…
Botulism is a rare but severe illness caused by a toxin that attacks the nervous system. All types of botulism can be fatal and are considered medical emergencies.
The most frequently contaminated foods are home-preserved vegetables or fruits, cured pork and ham, raw or smoked fish, and honey.
Botulism can also develop if the bacteria enters through wounds and produces the toxin there, like tetanus.