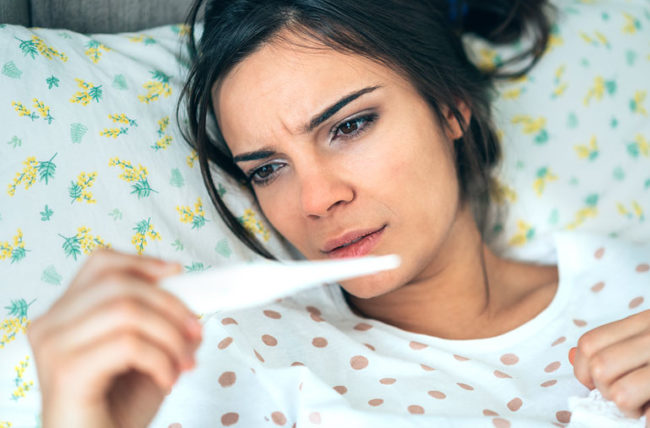
The average body temperature varies between 35.4 ° C and 37.2 ° C; however, it can vary in situations of flu or infection, such as pneumonia, for example. The main variations in body temperature include:
Slightly increased temperature, low-grade fever, or breakdown: between 37.4ºC and 38ºC. In these cases, other symptoms generally appear, such as chills, tremors or redness of the face, having to remove the first layer of clothing, take a warm bath, or drink water;
Fever: temperature above 38.1 ºC. In the case of adults, it is recommended to take a 1000 mg paracetamol tablet, put on only one layer of clothing and apply cold compresses to the forehead. If the temperature does not drop after 3 hours, you should go to the emergency room;
High fever: temperature above 39.6 ºC, which should be considered a medical emergency; for this reason, the person should be evaluated by a doctor.
Likewise, the temperature can also be lower than average, that is, lower than 35.4 ºC. This generally occurs when the person is exposed to the cold for a long time. In these cases, you should try to avoid the source of cold and wear several layers of clothing, drink hot tea, or heat the house, for example. See what hypothermia is, the main symptoms, and treatment.
See the video below for some strategies to lower a fever:
Representative image of the video
What is the fever temperature in infants and children?
The body temperature of the baby and the child is different from that of the adult, considering that the usual thing is for the temperature to vary between 36 ºC and 37 ºC, the value of the thermometer being evaluated as follows:
Slightly elevated temperature: between 37.1ºC and 37.5ºC. In these cases, a layer of clothing should be removed from the baby and given a warm bath;
Fever: anal temperature higher than 37.8 ° C or an axillary temperature higher than 38.5 ° C. In these cases, parents should consult the pediatrician to guide the use of medications for fever or the need to take the baby to the emergency room;
Low body temperature (hypothermia): temperature below 35.5 ºC. An extra layer of clothing should be placed on the baby, and drafts avoided in these cases. If the temperature does not rise in the next 30 minutes, the baby should be taken to the emergency room. See more about hypothermia in babies.
Variations in temperature in the baby are not always a cause of illness or infection and may be due to the amount of clothing placed, the birth of teeth, reaction to a vaccine, or the temperature of the environment.
Temperature Sensor: NTC Thermistor
Thermistors, from the English “thermistor” (Thermally Sensitive Resistor), are devices based on semiconductor materials whose resistance varies with temperature. If their coefficient of variation with temperature is negative, they are called NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient), while if it is positive, they are called PTC.
The foundation of thermistors is in the dependence of the resistivity of semiconductor materials with temperature due to the variation with is in the number of free carriers. As the temperature increases, in general, the number of free carriers also increases, thus reducing the resistance, hence the negative temperature coefficient. This dependence varies with the impurities, and if the doping is very intense, the material exhibits, in specific temperature ranges, metallic properties with a positive coefficient (PTC) in that range.
Like any device built based on semiconductors, Thermistors have some parameters that must be considered for their choice. The most frequently used terms are:
1. Zero power resistance: Thermistor resistance when there is no self-heating effect.
2. Variation of resistance with temperature: Sensitivity; typically 4Ohms / ° C.
3. Power dissipation constant: Power required for the thermistor to increase its temperature by one degree Celsius concerning the environment surrounding it.
4. Stability: Ability of a thermistor to maintain its characteristics within the range 0.03 ° C / year in 12 years.
5. Self-heating: Power dissipated in the thermistor.
6. Maximum operating temperature: Maximum temperature at which the thermistor will maintain its operation with acceptable stability characteristics (-75 ° C – 150 ° C).
As a summary, some of the most essential characteristics of thermistors are given:
-High sensitivity.
—High thermal coefficient.
—They have a variable response time.
“They suffer from self-heating.”
“They are not linear.”
“They are small in size.”
Protection against discharge and radio frequency
The signal input includes a 10K resistor pair to the current limitation. Neon lamps act as a voltage hold circuit, limiting it to around 100V. Neon lamps are chosen for their low capacitance and high impedance to direct current. The resistors in series with the diodes form a holding circuit as second protection for the input amplifiers. Two passive RC filters are used to reduce susceptibility to Radio Frequency (See Figure 2).
Current source and scaling
It consists of a two-stage amplifier designed to obtain a voltage proportional to the temperature in degrees Centigrade (from 0 to 5volts in a range from 0 to 50ºC). Two adjustment potentiometers are available for zero and full scale.
Rectal temperature measurement
Baby lying face down on lap with a thermometer inserted into the rectum
The rectal temperature method works best in infants and young children. Older children may resist having something put in their anus.
If using a glass thermometer, hold the top and shake it until the line is below 99 ° F (37.2 ° C)
Before you measure the child’s temperature, make sure that they are relaxed. Place your tummy child on a comfortable surface, such as a bed or chair.
Before inserting the thermometer:
- Make sure it is clean.
- Wash it off with soap and warm water.
- Coat the end of it with petroleum jelly.
This will facilitate the insertion
Gently insert the thermometer about 1 inch (2 cm) into your child’s rectum. If you encounter any resistance, pull the thermometer back a little. Never force the thermometer to try to overcome a resistance. Doing so could damage the intestinal wall.
Keep your child still while the thermometer is in place
Leave the glass thermometer in your child’s rectum for two minutes; then take it out. If it’s a digital thermometer, pull it out when you hear the signal (usually a beep or series of beeps)
Read the temperature. If you are using a glass thermometer, you may need to rotate it to see the end of the line
Turn off the thermometer, wash the tip with soap and warm (not hot) water, and rinse with alcohol. Dry it well