The need to separate the gathering phase from the cutting phase itself is bioscience.
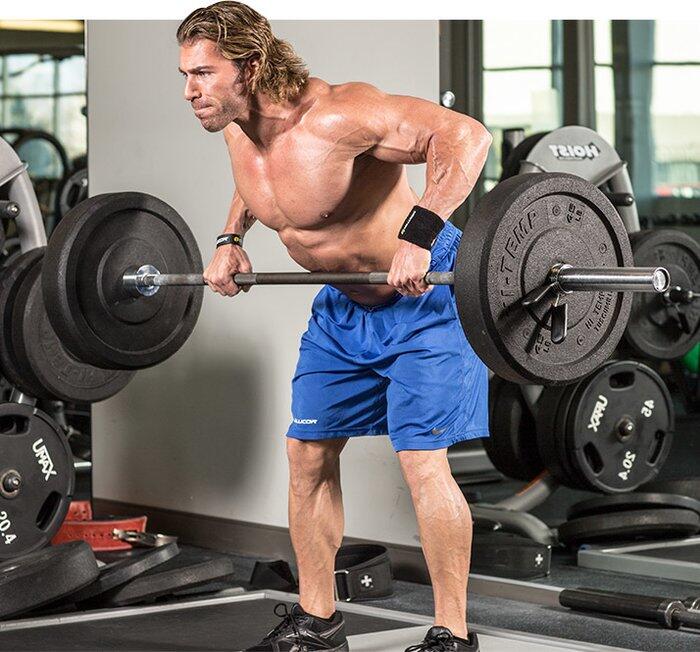
Your body may be in a state of anabolism or catabolism. In the way things are done, bulking is anabolic, so you trick your body into thinking that you are building it and growing. And the cut is catabolic, so you reduce your calorie intake, and your body begins to lose fat (and muscle) because it breaks down to survive.
But why would you want to be catabolic? Ideally, your muscles will continue to grow, but you will be burning fat. Burning fat doesn’t have to be catabolic for the rest of your body!
Is this so difficult to achieve? No, it is not. All you have to do is trick your body into treating its fat stores as an external food supply rather than a part of itself.
The best way to do this is by adopting a ketogenic diet. There is a lot at stake here. Replacing your carbohydrate intake with fat means that your body produces more growth hormone, and not having carbohydrates tricks your body into thinking that you are starving. That tricks your body into holding onto lean muscle mass. And if you have an adequate protein intake, it causes a rapid increase in muscle mass!
Does lifting heavy every other day and warming up from bodyweight training every morning train me too much?
Is it better to run 5 miles at a steady heart rate or a steady pace?
What are some good blogs or websites to read and learn about essential weightlifting?
What level of fitness is required to hike Mount Kenya?
Besides barbell deadlifts, what is the next best exercise someone can do without access to the lower back and rear chain bars?
So yes, it is entirely possible to build muscle while cutting fat! All you have to do is trick your body into using fat as a fuel source to fuel your muscles!
The effects of the ketogenic diet on skeletal muscle and fat mass
Take a look at this research article. Twenty-six trained people were used in a study to test this. Half of them replaced their carbohydrates with fat with no calorie deficit. So they didn’t try to bulge or cut; they just changed their diet for 11 weeks.
The keto group put on 4.3 kg of muscle and lost 2.2 kg of fat on average. The control group put on 2.2 kilos of muscle and lost 1.5 kg of fat on average.
They gained more muscle and lost more fat!
The ketogenic diet does not affect strength performance in elite artistic gymnasts.
Elite gymnasts could reduce their body fat levels to 5% (on average, this real-life !!!) without a deficit of calories or loss of strength for three months simply by adopting such a diet! And if you scroll down to the muscle gain section, you’ll see that there was a slight, almost negligible increase of 0.3 kilos of lean muscle. If you think about it, these folks are elite-level national athletes who train in gymnastics without worrying about “bulking up” and getting past the rookie winning stage. 0.3 kg of muscle for three months is hyuuuuuuge!
Process 6 Days
HydrationWater consumption should be high for the first three days, drinking around 3-5 litres/day and preferably between meals. This hydration will be with water of low sodium content.
Upon reaching the three days before the competition, we will gradually lower the amount of water, drinking a maximum of ½ litre/day on the eve of the event.
Hyper-protein diet.
We will maintain a high protein diet for the first three days that can reach up to 4.5 gr/kg of lean body weight.
Decreased sodium in the dietFoods rich in sodium should be avoided and cooked with salt but forcing the distillation of food until the last three days before the event should be avoided to not give rise to hormonal rebounds that could lead to water retention at the last minute.
Contribution of water-soluble vitamins.
Vitamin C and Group B are eliminated in the urine, and any excess never accumulates in the body; Thus, the mega doses of Vitamins B and C have the task of forcing the urinary excretion of them, helping to eliminate any subcutaneous water retention.
Carbohydrate Loading and UnloadingInside the muscle, glucose is stored in the form of glycogen. For every one gr. of stored glycogen are stored between 2.8 to 3 grams. Of water too. In the first three days, these muscular deposits are emptied through thorough training and a gradual decrease in the carbohydrate content of the diet (especially flours and fruits), being able to consume the tertiary day a minimum of 40 gr. Carbohydrates. In the last three days, you have to gradually increase the carbohydrate content of the diet until it represents 70% of the total calories.
Accompanying this carbohydrate overload, water consumption is gradually cut back to ½ litre per day. As carbohydrates need water to be stored as glycogen and we seek to cut back on their intake, the body will be forced to take water from a surplus, in this case, from the subcutaneous tissue.
Sodium dischargeThe elimination of sodium in the diet (to eliminate water retention) will be done until the last three days and will be done by washing the food before cooking, and hydration will be done with distilled water.
Fat LoadFat is a nutrient whose presence in the blood is maintained for 48 to 72 hours before disappearing from it. Its presence in the blood forces the passage of water into the vascular interior to dilute the excess blood viscosity so that the water used will be retained in the subcutaneous tissue (forcing muscle definition). The contribution of extra fat (olive oil, almonds, avocado, etc.) is made abundantly two days before the event to ensure this effect.
Diuretic Substances.
From the beginning of the preparation, it would be desirable to introduce some natural diuretic preparation that optimizes the diuretic phenomena in this phase. The choice would be Horsetail and Goldenrod, which, unlike pharmacological diuretics, do not set in motion hormonal counter-regulatory mechanisms that can promote rebounds and last-minute water retention.
LoadAfter depletion, the loading phase follows for competition. Loading means putting potassium into the muscle cell tissues in the first place to increase the volume of water inside the cells; this is because potassium is responsible for controlling the entry of intracellular fluid. In this way, we drag any remaining subcutaneous water into the cells, leaving the skin attached to the muscle to give the lean appearance. This load is done by taking potassium supplements and foods rich in simple carbohydrates that help you transport them (grapes, plums, kiwi, etc.).
The load that is made of simple, complex carbohydrates and proteins; is done by eating balanced portions of simple and fibrous carbohydrates every hour or two hours; the proteins could be lean beef, chicken, protein powders, and never fish so as not to retain water and maintain only the minimum necessary amount of water.